Age requirements for free and compulsory education help policymakers ensure that students receive the benefits of early education and support a reduction in dropout rates. Depending on the state, students are required to attend school for as few as nine years and up to 13 years. However, exemptions exist on both sides of the K-12 spectrum to support students with circumstances outside of compulsory attendance requirements. Some common exemptions include home instruction, mental or physical conditions that make attendance infeasible, or completion of equivalent high school requirements.
This resource provides a national comparison of school age requirements for both free and compulsory education across all 50 states and the District of Columbia. Unless otherwise noted, all information in this resource was gathered from state statutes and constitutions only.
Definitions
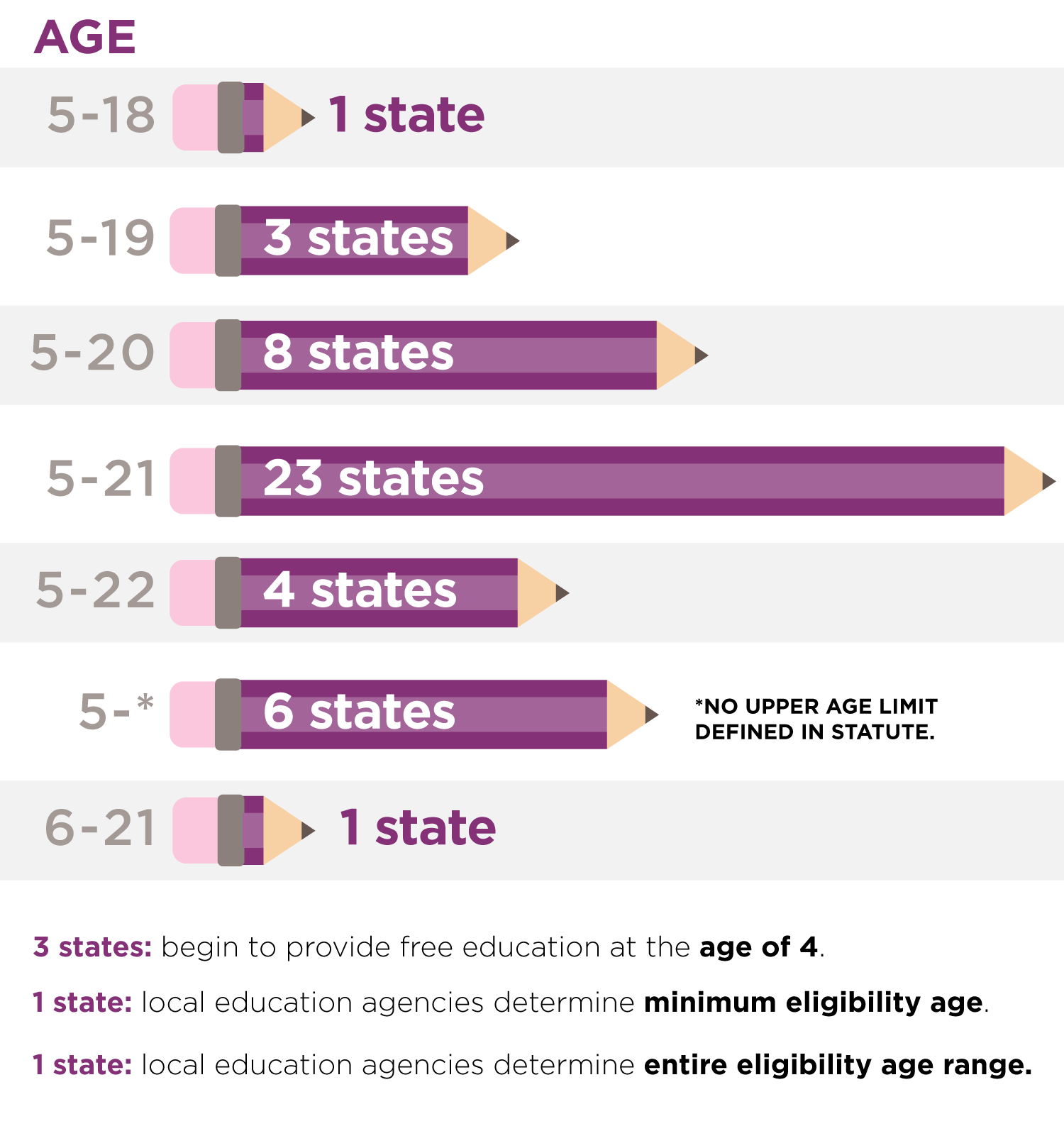
- Age Requirement for a Free Education refers to the years in which a student must be admitted into a public school free of charge.
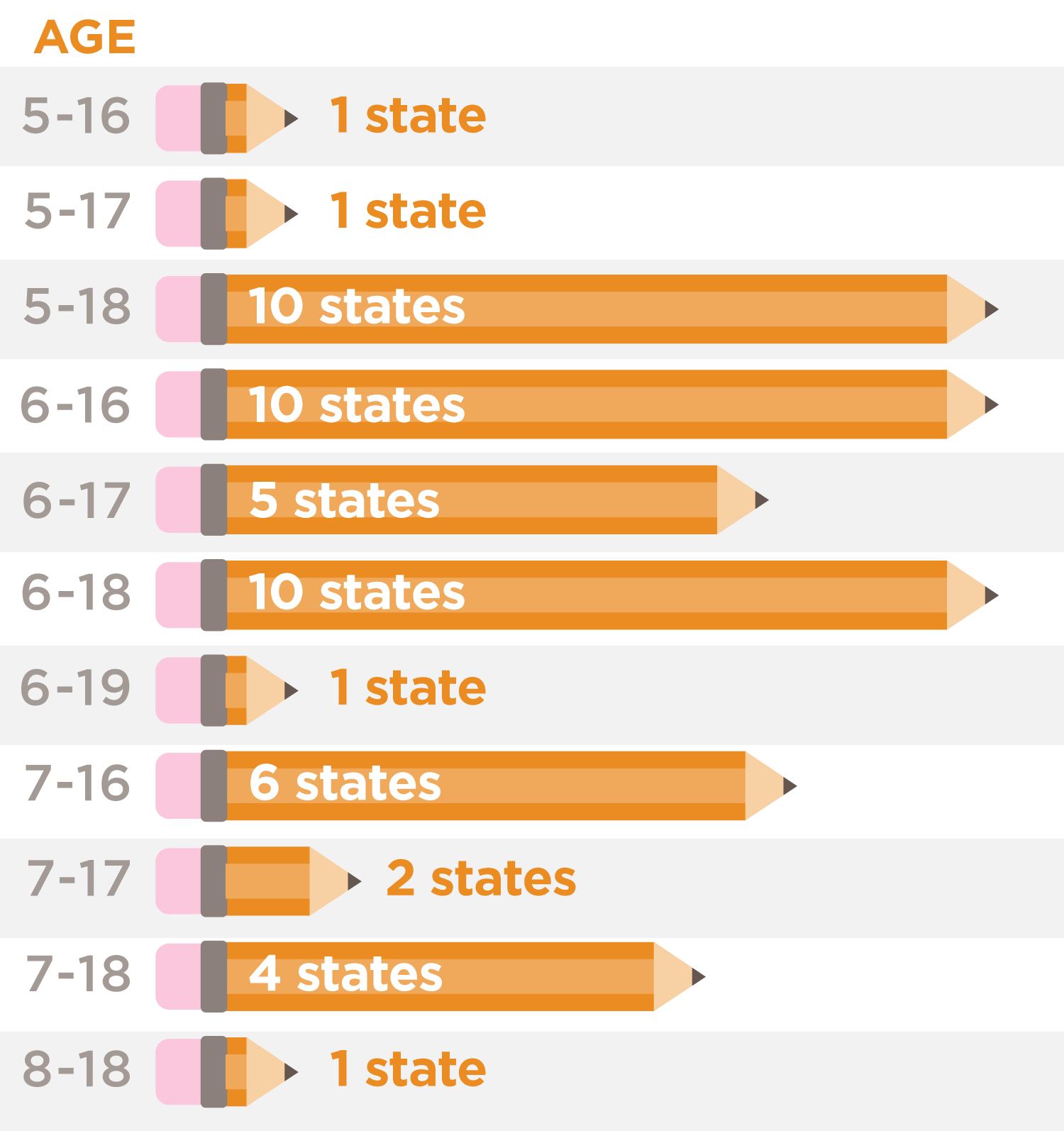
- Age Requirement for Compulsory Education refers to the years in which a student is required to attend school or an equivalent program defined by law.
- Unique exemptions impacting the compulsory school age will be included in the notes section.
- Lower and Upper Age Limits
- The lower age used is the minimum age a student must have turned to be provided with free education or to be required to attend school.
- The upper age used is the maximum age a student is eligible for free education or is required to attend school.
- An age range of 5-21 refers to a student who has turned five years of age but has not yet turned 21 years of age.
- “None identified in statute”: When used in place of an upper age limit, this means that no cutoff age or upper age limit was explicitly listed in state policy regarding the general student population. In some states, an upper age limit is provided for specific student populations, such as special education students.